Attic Greek Aorist Tense

Present imperfect future aorist the equivalent of past simple perfect pluperfect and future perfect.
Attic greek aorist tense. By contrast in theoretical linguistics tense refers to a form that specifies a point in time past present or future so the aorist is a tense aspect combination. Greek verb tenses intermediate discussion no element of greek language is of more importance to the student of the new testament than the matter of tense a variation in meaning exhibited by the use of a particular tense will often dissolve what appears to be an embarrassing difficulty or reveal a gleam of truth which will thrill the heart with delight and inspiration. This is the most common tense for referring to. This article therefore chiefly describes.
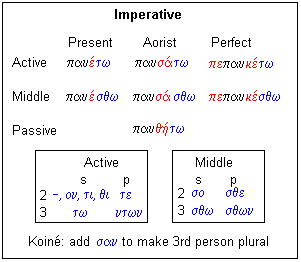
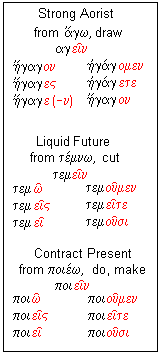
Ancient greek verbs have four moods indicative imperative subjunctive and optative three voices active middle and passive as well as three persons first second and third and three numbers singular dual and plural. This is one of the basic points we try to make in first year greek but in the rush to simplify the language sufficiently for a first year student sometimes the subtly of this point is missed. Greek verbs and infinitives can express all three aspects but the most common are. Abbreviated aor verb forms usually express perfective aspect and refer to past events similar to a preterite.
It is also used for events. While both the imperfect and aorist tenses refer to past actions and so are past tenses they differ in aspect. Ancient greek grammar had the aorist form and the grammars of other indo european languages and languages influenced by the indo european grammatical tradition such as middle persian sanskrit armenian the south slavic languages and georgian also. And yet the aorist is so much more than past time and in fact.
Wikipedia has a nice summary of the aorist and more details can be found in the the article on the ancient greek aorist in particular. εἰμί in liddell scott 1889 an intermediate greek english lexicon new york. Just to be clear i still believe the augment indicates past time. In the indicative mood there are seven tenses.
εἰμί in autenrieth georg 1891 a homeric dictionary for schools and colleges new york. εἰμί in liddell scott 1940 a greek english lexicon oxford. Greek expresses this aspect by using the present stem e g the present and imperfect tense completed. It is used for undivided events such as the individual steps in a continuous process narrative aorist.
I haven t gone over to the other camp on this point. If you remember that the meaning of the word perfect is complete then you can remember that the perfect tense has to do with completed action but the perfect tense is a primary tense because it emphasizes the present or ongoing result of a completed action the perfect tense in greek corresponds to the perfect tense in english and is illustrated in the following sentences. εἶμαι eîmai modern greek. This is from the first link.
This is an action that took place over an extent of time was habitual or was more than a single action in some way. The literary greek of athens in the fifth and fourth centuries bc attic greek was the standard school room form of greek for centuries. Aorist ˈ eɪ ə r ɪ s t. The aorist tense always conveys a single discreet action i e.